In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, efficiency and precision are paramount. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) serve as a cornerstone for maintaining quality, consistency, and safety. But as workplace dynamics evolve, a critical question emerges: Are traditional text-based SOPs the most effective way to train employees and ensure adherence to protocols? Neuroscience says no. Research overwhelmingly supports the shift from written procedures to visual SOPs. Here, we explore 10 neuroscience-based statistics that demonstrate why visual SOPs are superior.
1. 90% of Information Transmitted to the Brain Is Visual
The human brain is inherently wired for visual processing, a trait deeply rooted in evolution. From recognizing predators to navigating complex environments, humans have relied on their ability to process visual stimuli quickly and effectively. According to neuroscience studies, an astounding 90% of the information transmitted to the brain is visual. This means that the brain prioritizes and excels at interpreting images, colors, patterns, and motion over text-based inputs.
Visuals are not only processed faster but also more efficiently than written words. The brain\u2019s visual cortex, responsible for decoding visual inputs, is highly adept at recognizing and interpreting complex visual information almost instantaneously. This capability makes visuals an exceptionally powerful medium for conveying intricate instructions, especially in professional settings where precision and speed are critical.
In the context of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), the integration of images, videos, and diagrams into instructional materials can transform how employees absorb and apply information. Unlike dense blocks of text that require careful reading and interpretation, visuals provide immediate clarity and context. A step-by-step video showing how to operate machinery, for example, eliminates the guesswork often associated with textual instructions, enabling employees to follow processes with confidence and accuracy.
Furthermore, visuals transcend language barriers, making them universally understandable across a diverse workforce. Employees from different linguistic or educational backgrounds can grasp visual instructions without the need for extensive translations or supplementary explanations, fostering inclusivity and reducing training time.
Why It Matters: Visual SOPs align seamlessly with the brain\u2019s natural preference for visual data. By leveraging this inherent strength, organizations can ensure faster comprehension, better retention, and significantly reduced errors. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also empowers employees with clear, actionable guidance tailored to how the brain works best.
Source: Medina, J. (2008). Brain Rules: 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and School. Pear Press.
2. Humans Process Visuals 60,000 Times Faster Than Text
The brain’s ability to process visuals is nothing short of remarkable. Research suggests that visuals are processed approximately 60,000 times faster than text. This rapid processing speed is rooted in the way the brain prioritizes and decodes visual information, bypassing the slower and more effort-intensive process of reading and interpreting text. When presented with an image, diagram, or video, the brain can immediately identify patterns, recognize key elements, and derive meaning without the need for conscious translation into words.
In the workplace, this neurological advantage has profound implications, particularly in the use of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). A visual SOP allows employees to understand instructions almost instantaneously, providing clear and direct guidance that eliminates confusion or hesitation. This is especially critical in fast-paced manufacturing environments, where delays caused by misinterpretation of written instructions can disrupt workflows and lead to costly errors.
By replacing dense, text-heavy SOPs with visuals such as step-by-step videos or annotated diagrams, organizations enable their teams to act swiftly and decisively. Visual SOPs reduce cognitive load, allowing employees to focus their mental energy on task execution rather than deciphering instructions.
Impact: The brain’s ability to process visuals faster directly translates to quicker task execution and reduced downtime. This not only boosts productivity but also ensures a smoother, more efficient workflow in manufacturing and operational settings.
Source: 3M Corporation. (1982). Studies in Visual Communication.

3. Visuals Improve Retention by 42%
Studies reveal that individuals retain 42% more information when it is presented visually compared to text alone. This significant difference is rooted in the brain's ability to store and recall images more effectively than words. Visual information engages multiple cognitive pathways simultaneously, creating stronger neural connections that lead to better memory retention. In contrast, written instructions often require extensive mental effort to process, making it harder to recall details, especially for complex or lengthy procedures.
For Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), this means that traditional text-based formats often fail to make a lasting impression on employees. Lengthy paragraphs of text can be overwhelming and are prone to being skimmed or misunderstood, leading to inconsistent application of instructions. However, incorporating visual elements like flowcharts, step-by-step videos, or annotated images makes the content more digestible and easier to remember.
Visual SOPs also cater to how memory works best: through association and pattern recognition. By linking instructions with visual cues, employees are more likely to recall the correct processes when performing tasks, even under pressure or in high-stakes scenarios.
Key Takeaway: Enhanced retention rates from visual SOPs ensure that employees are consistently well-prepared to execute tasks with precision and accuracy. This not only improves operational outcomes but also builds confidence in the workforce, fostering a culture of reliability and consistency.
Source: Levie, W. H., & Lentz, R. (1982). Effects of text illustrations: A review of research. Educational Communication and Technology Journal.
4. People Follow Visual Instructions 323% Better Than Written Ones
A study published in the journal Applied Cognitive Psychology demonstrated that individuals perform tasks 323% better when guided by visuals instead of written instructions. This staggering improvement highlights the profound impact of visuals on task execution. By simplifying complex procedures and presenting information in an intuitive, easy-to-follow format, visuals eliminate ambiguity and enhance comprehension.
In manufacturing environments, where precision and accuracy are non-negotiable, this advantage can mean the difference between seamless operations and costly errors. Written instructions often leave room for misinterpretation or require excessive cognitive effort, whereas visual guides provide clarity and directness that accelerate learning and improve execution.
Visual SOPs tap into the brain with the ability to process and apply information in real-time. For tasks involving detailed or intricate steps, such as operating machinery or following safety protocols, visuals significantly reduce the likelihood of mistakes by presenting information in a way that is immediately actionable.
Example in Practice: A step-by-step video demonstration of machine calibration enables employees to follow the procedure with confidence and accuracy, resulting in dramatically fewer errors compared to relying on a dense, text-based guide. This practical application underscores the essential role of visual SOPs in boosting performance and ensuring consistency in high-stakes environments.
Source: Waller, R. (1981). Understanding Visual Instructions. Applied Cognitive Psychology Journal.
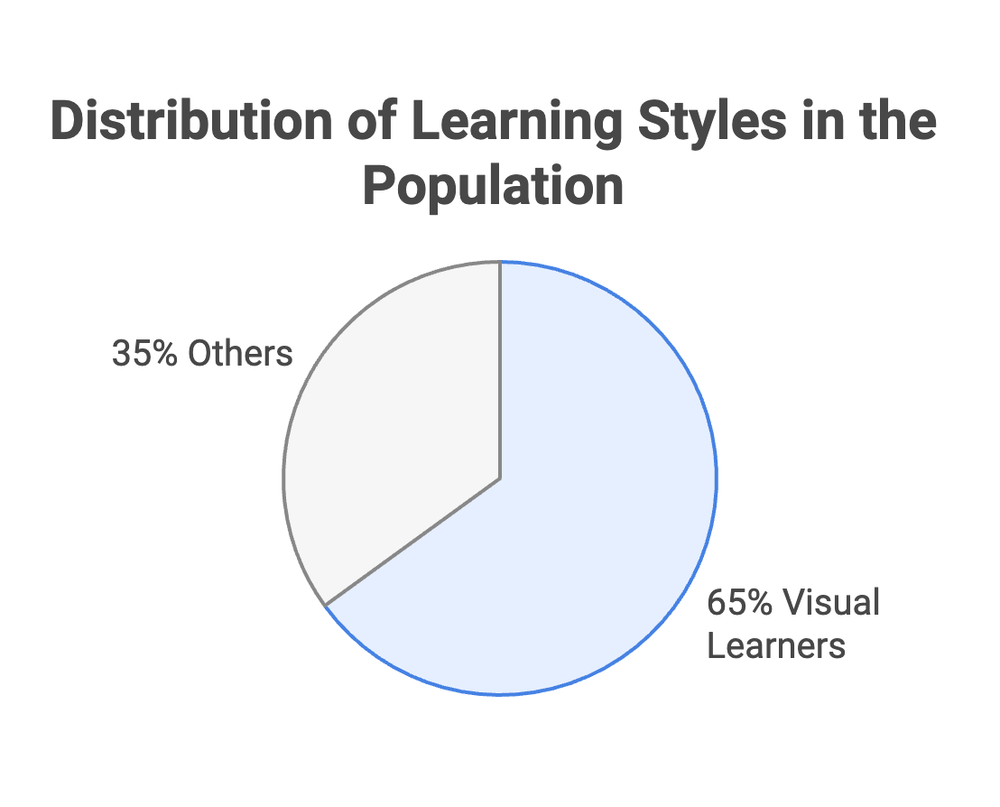
5. 65% of the Population Are Visual Learners
Approximately 65% of individuals are classified as visual learners, meaning they absorb and retain information more effectively when it is presented in a visual format. This dominant learning style reflects the brain's preference for visual stimuli, such as images, diagrams, and videos, which are processed faster and stored more efficiently in memory. Despite this, traditional text-based SOPs predominantly cater to verbal learners, who make up only a smaller portion of the population. This leaves a significant segment of the workforce struggling to interpret and remember critical instructions.
The limitations of text-based SOPs can lead to misunderstandings, inconsistent task execution, and increased errors, especially for those who rely heavily on visual learning. For example, an employee who learns best by seeing a demonstration may find it challenging to follow a dense, text-heavy manual, resulting in slower performance or mistakes.
Solution: Visual SOPs provide a more inclusive approach by catering to diverse learning styles, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. By incorporating videos, infographics, and step-by-step visuals, organizations can ensure that training materials resonate with a broader audience. This not only improves understanding and retention but also boosts engagement and confidence, creating a more effective and equitable learning environment for all employees.
Source: Bruner, J. S. (1966). Studies in Cognitive Growth. Wiley.
6. The Brain Decodes Visual Data in 13 Milliseconds
Research shows that the brain can interpret visual data in as little as 13 milliseconds, highlighting its remarkable ability to process images almost instantaneously. This rapid interpretation capability allows visuals to convey complex information in a fraction of the time it would take to read and comprehend text. The brain’s efficiency in decoding visual stimuli is one of the key reasons why visuals are so effective for learning and communication.
In the workplace, this speed translates into significant time savings when using visual SOPs. Employees can quickly scan visual instructions, such as diagrams or videos, and grasp the required steps without the need to decipher lengthy text-based guides. This is especially valuable in fast-paced environments like manufacturing, where quick comprehension can directly impact productivity and minimize downtime.
Visual SOPs not only streamline the learning process but also reduce cognitive load, allowing employees to focus on execution rather than interpretation. This ensures that tasks are completed more efficiently and with fewer errors, benefiting both individual performance and overall operational effectiveness.
Benefit: The brain’s ability to process visuals rapidly leads to enhanced efficiency in both training and on-the-job execution. Visual SOPs empower employees to perform tasks with speed and accuracy, ultimately driving productivity and improving workflow.
Source: MIT, In the blink of an eye